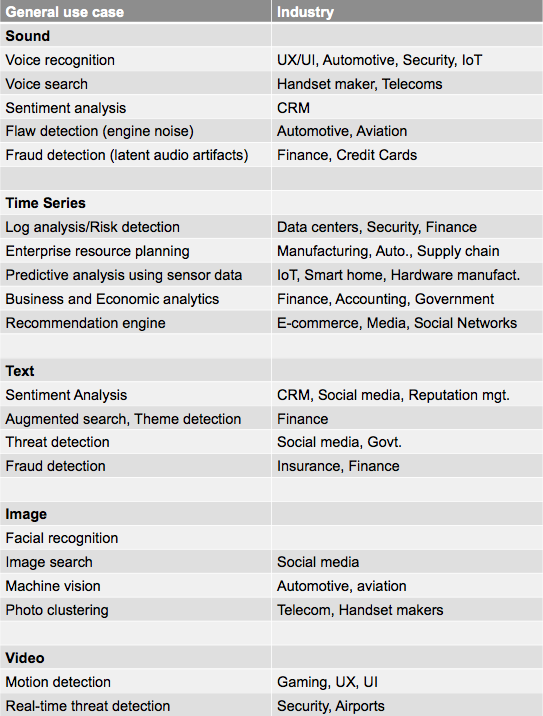
Deep Learning, Machine Learning & AI Use Cases
Deep learning excels at identifying patterns in unstructured data, which most people know as media such as images, sound, video and text. Below is a list of sample use cases we’ve run across, paired with the sectors to which they pertain.
Feature Introspection
Traditional machine learning has the advantage of feature introspection – that is, it knows why it is classifying an input in one way or another, which is important for analytics. But that very advantage is what excludes it from working with unlabeled and unstructured data, as well as attaining the record-breaking accuracy of the latest deep learning models. Feature engineering is one of the major chokepoints of traditional machine learning, since so few people are able to do it well and quickly enough to adapt to changing data.
For cases where feature introspection is necessary (e.g. the law requires that you justify a decision to, say, deny a loan due to predicted credit risk), we recommend using a deep net in an ensemble with machine-learning algorithms, allowing each one to vote and relying on each for its strength. Alternatively, one can perform various analyses on the results of deep nets to form hypotheses about their decision-making.
Learn to build AI in Simulations »
Text
Named-entity recognition
One use of deep-learning networks is named-entity recognition, which is a way to extract from unstructured, unlabeled data certain types of information like people, places, companies or things. That information can then be stored in a structured schema to build, say, a list of addresses or serve as a benchmark for an identity validation engine.
Speech-to-Text
With the proper data transforms, a deep network is capable of understanding audio signals. This can be used to identify snippets of sound in larger audio files, and transcribe the spoken word as text.
Image
Object recognition
Object recognition is an algorithm’s ability to identify arbitrary objects – such as balls, animals, or even faces – within larger images. This is typically used in engineering applications to identify shapes for modeling purposes. It’s also used by social networks for photo tagging. Facebook’s Deep Face is a good example of a deep-learning application in this realm.
Machine Vision + Natural-Language Processing
Advances in reality capture and reality computing are making virtual and real worlds converge. One application of deep learning to this newly available data is to recognize and label objects in 3D environments, and in real life.
From there, it’s a short step to simulated semantics, in which machines learn the nature and constraints of objects in the world, through their virtual representations, and then bring that understanding to the language they generate and ingest. We believe that is one of many futures in store for neural nets.
